How to Choose Metal Seal Rings: A Comprehensive Guide for Industrial Applications
Metal seal rings are critical components in high-performance industrial systems, renowned for their exceptional temperature resistance and corrosion-resistant properties. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process of selecting the optimal metal seal ring for your specific application, ensuring precise installation and peak performance in demanding environments.
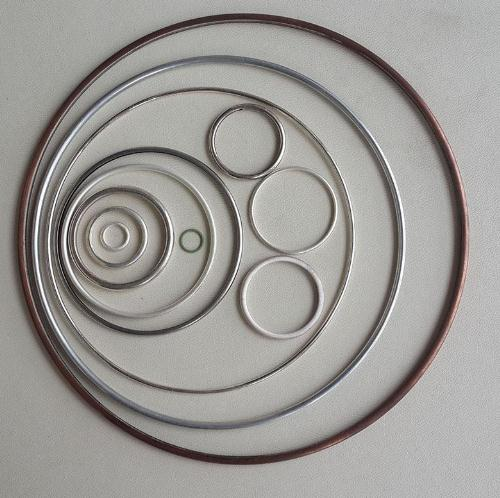

Key Factors in Selecting the Right Metal Seal Ring
- Groove Specifications and Tolerances:
- Accurately measure and analyze the groove dimensions, including diameter, width, and depth.
- Consider tolerance stack-up to ensure a precise fit and prevent installation issues.
- Typical tolerance ranges for industrial applications: ±0.001" to ±0.005" (0.025mm to 0.127mm).
- Application-Specific Requirements:
- Operating temperature range: From cryogenic (-270°C) to extreme heat (up to 1000°C).
- Pressure conditions: Vacuum to ultra-high pressure (up to 300 MPa or 43,500 psi).
- Chemical compatibility with process media.
- Dynamic vs. static sealing requirements.
- Material Selection:
- Common materials: 316L Stainless Steel, Inconel 718, Hastelloy C-276.
- Consider factors such as corrosion resistance, yield strength, and thermal expansion.
- Surface Finish Requirements:
- Typical surface finish for metal seal applications: 16-32 μin Ra (0.4-0.8 μm Ra).
- Smoother finishes may be required for ultra-high vacuum or high-pressure applications.
Advanced Features of High-Performance Metal Sealing Rings
- Precision Manufacturing Techniques:
Metal sealing rings are fabricated using state-of-the-art processes, including:
- High-precision CNC machining with tolerances as tight as ±0.0005" (0.0127mm).
- Advanced welding techniques for seamless or longitudinally welded configurations.
- Specialized heat treatment processes to optimize mechanical properties.
- Extreme Temperature Capabilities:
Engineered to perform in a wide range of temperatures:
- Cryogenic applications: Down to -270°C (-454°F).
- High-temperature environments: Up to 1000°C (1832°F) with specialized alloys.
- Ability to maintain sealing integrity during rapid temperature fluctuations.
- Enhanced Material Properties:
Utilization of high-performance alloys offers:
- Superior corrosion resistance in aggressive chemical environments.
- High yield strength, typically ranging from 30 ksi to 150 ksi (207 MPa to 1034 MPa).
- Excellent fatigue resistance, with some designs capable of over 100,000 cycles.
- Versatile Sealing Solutions:
Adaptability to various industrial challenges:
- Static sealing with leak rates as low as 1 x 10^-10 cc/sec helium.
- Dynamic sealing capabilities for rotating and reciprocating equipment.
- Custom designs for unique application requirements.
Key Advantages of Metal Sealing Rings in Industrial Applications
- Exceptional resistance to high temperatures and pressures, outperforming elastomeric seals in extreme conditions.
- Superior chemical compatibility, suitable for use with aggressive media in petrochemical and pharmaceutical industries.
- Extended service life, often exceeding 10 years in properly designed systems.
- Ability to maintain sealing integrity under dynamic loads and vibrations.
- Low outgassing properties, crucial for semiconductor and aerospace applications.
- Radiation resistance for nuclear and medical imaging equipment.
Critical Applications of Metal Sealing Rings
Metal sealing rings are indispensable in various high-stakes industries, including:
- Oil and Gas: Wellhead equipment, subsea valves, and high-pressure processing units.
- Aerospace: Jet engine seals, hydraulic systems, and spacecraft propulsion.
- Chemical Processing: Reactors, heat exchangers, and corrosive media handling systems.
- Power Generation: Steam turbines, nuclear containment, and high-temperature gas handling.
- Semiconductor Manufacturing: Ultra-high vacuum chambers and gas delivery systems.
- Cryogenics: LNG processing, superconducting magnets, and space simulation chambers.

 Language
Language
 China
China German
German French
French Italian
Italian Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Arabic
Arabic Dutch
Dutch


 Service
Hotline
Service
Hotline